Table of contents
Mitochondria: how to activate your body's energy factories when exhausted
How energetic you feel does not start in your head but in your cells. Each cell in your body contains an average of 500 to 2,000 mitochondria. They are descended from parasites and entered the cells of our 'ancestor organisms' about a billion years ago. In exchange for fuel for the cells, the cells give mitochondria shelter.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are molecular energy factories. They are busy 24/7 converting food into building materials. Your body can make 3 types of fuel from food. Proteins are converted into amino acids, fats are converted into fatty acids and sugars are chopped up. This produces glucose. Body cells get their energy mainly from burning glucose. Mitochondria burn glucose creating ATP. ATP is fuel for your cells and is used throughout your body.
Free radicals
If you have a healthy lifestyle, your mitochondria can do their job well and you feel energetic. However, as with almost all manufacturing processes, the production of ATP releases so-called 'by-products'. These free radicals can cause damage in your body. Fortunately, healthy mitochondria can handle a normal amount of free radicals just fine. But when there are too many free radicals floating around in your body - either because there are too few mitochondria or because the mitochondria present are not functioning properly - some of them will cause damage. This is called oxidative stress and causes a steady deterioration of your body. But how then does the function of mitochondria become impaired?
Disrupted function
The function of mitochondria can be disrupted in many ways. For example:
- smoking
- an unbalanced eating pattern
- a lack of physical activity or, on the contrary, excessive physical exertion (top-class sport)
- insulin dysregulation (metabolic syndrome, diabetes, obesity)
- chronic (silent) inflammation (as in rheumatism, psoriasis)
- infections (e.g. Pfeiffer's disease, Lyme disease, HIV)
- (be)radiation from wireless devices such as smartphones and excessive exposure to sunlight and cosmic radiation (flying)
- toxins including heavy metals and pesticides
- certain medications such as ibuprofen, diclofenac and antibiotics
Tips to improve your mitochondria
As you can see, your mitochondria can be thwarted in many ways from performing their important task: providing your body with energy to realise your dreams. Fortunately, you can support your cells' energy factories. The better you do, the less exhausted you'll feel.
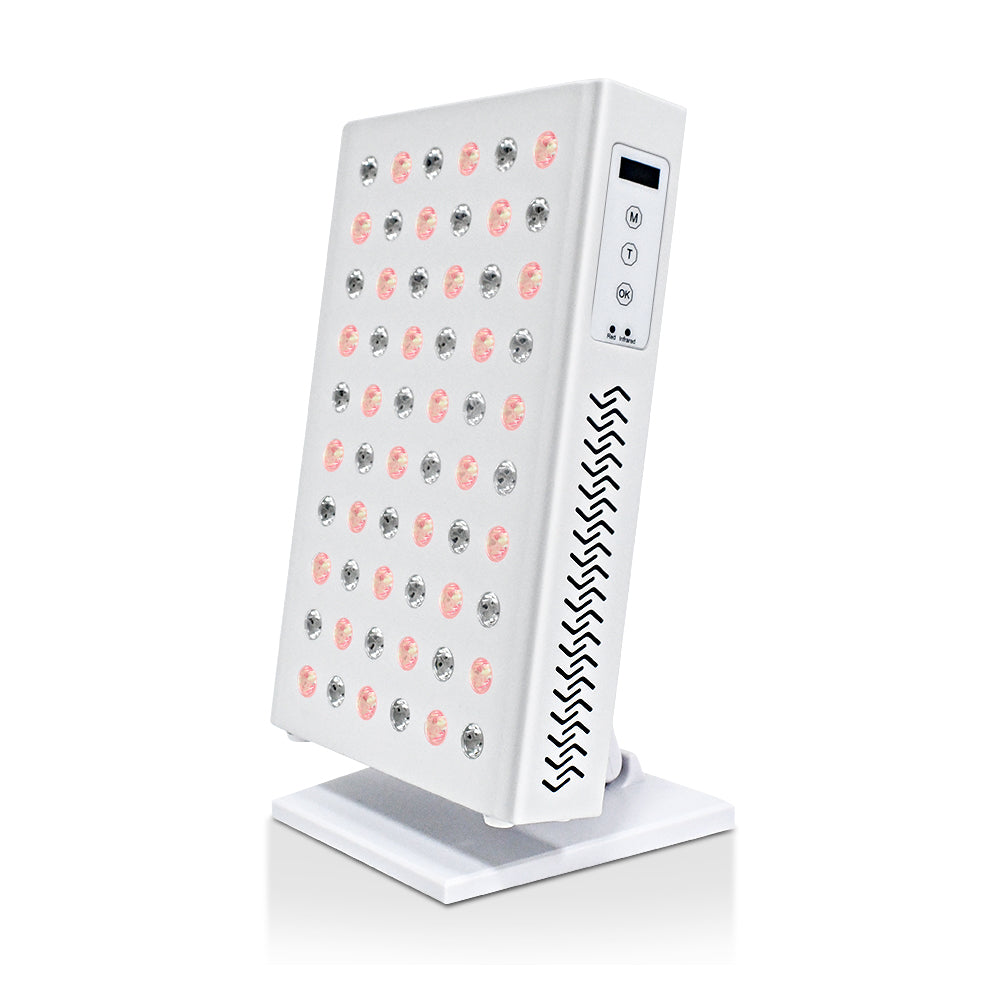
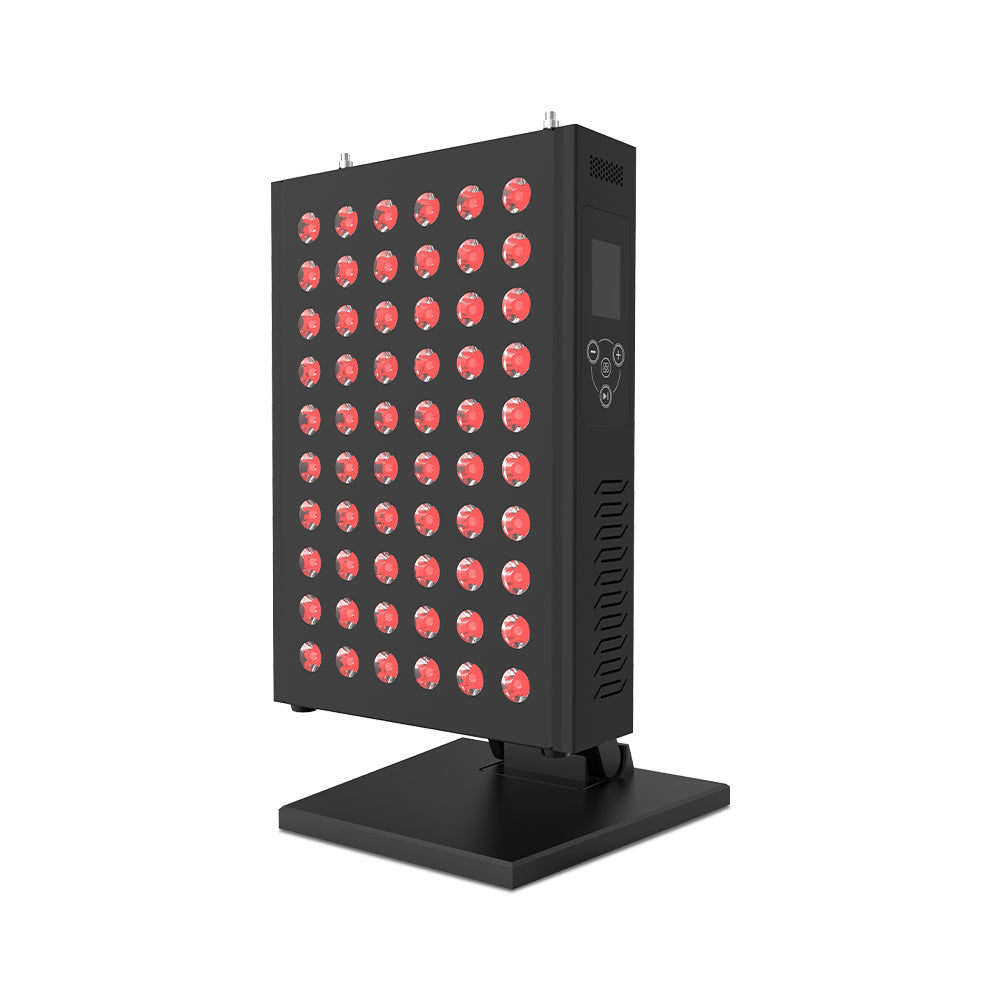
Boosting your mitochondria?
Then red light therapy is for you. Daily 10-minute baths in red light give your cells a huge boost. This is because the light penetrates to the core of the cell. There is much debate among scientists about all kinds of health topics, but not about red light, which is proven to be health-promoting.